“As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.”
What Is Type 2 Diabetes?
It is a chronic illness that prevents your body from adequately utilising insulin.
Insulin resistance is a feature of type 2 diabetes patients.
This kind of Diabetes most commonly affects people in their forties or older.
Adolescent Diabetes used to be called it.
But type 2 diabetes affects children and adolescents, mainly due to being overweight.
Diabetes Type 2 is the most frequent:
Type 2 diabetes affects over 29 million Americans.
84 million people have prediabetes, elevated blood sugar but not Diabetes.
Diabetes 2 Symptoms:
Type 2 diabetes symptoms might be so subtle that you miss them.
Around 8 million individuals with it are unaware.
• Unhealed wounds
• Reoccurring yeast infections
• Unwanted weight loss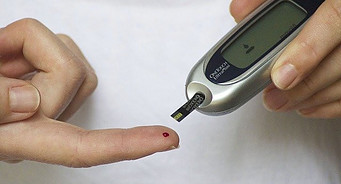
• Feeling hungry
• Unwanted weight loss
See your Doctor if…:
See your doctor if you experience black rashes on your neck or armpits.
Insulin resistance is indicated by acanthosis nigricans (black spots).
Type 2 Diabetes Causes Insulin is produced by your pancreas.
It aids in converting glucose (a kind of sugar) into energy in your cells.
The body produces insulin, but the cells don’t utilise it properly.
Initial Insulin Production:
Initial insulin production is increased to attempt to obtain glucose into cells.
But it can’t keep up, and glucose builds up in your blood.
Type 2 diabetes is usually caused by many factors.
Some examples are:
• Genes. Scientists discovered DNA sequences that influence insulin production.
• Added lbs Diabetes is a metabolic condition caused by excessive insulin production.
Metabolic Syndrome:
Metabolism Insulin resistance is linked to
- High blood sugar
- Abdominal Fat
- Blood Pressure

- Cholesterol
- Triglyceride levels
- Excessive liver glucose Low blood sugar causes the liver to produce glucose.
Following a meal, your blood sugar rises, and your liver slows down, storing glucose.
But not everyone’s livers. They keep having sugar.
• Ineffective cell communication:
Cells can misfire or misread signals.
They can affect how your cells create and utilise insulin or glucose.
• Beta-cell damage:
Misfiring insulin-producing cells cause blood sugar imbalances.
High blood sugar might also harm these cells.
Factors Associated with T2D Type 2 diabetes is caused by many factors.
The more you fit into this category, the better. A few things are personal:
• 45+
• Family
• Ethnicity
• A diabetic parent, sibling, or brother or Pacific Islander.
American?
American Your health and medical history may include risk factors like:
• Low HDL (“good”) cholesterol
• High triglycerides
• Prediabetes
• PCOS Mood Daily activities and lifestyle choices are other risk factors.
You can help with these:
Smoking, stress, and little or excessive sleep Detecting Type 2 Diabetes.
Your doctor can check for indicators of type 2 diabetes.
To confirm the diagnosis, they usually test you again.
One test may be enough if your blood glucose is high, or you have many symptoms.
• A1c. It’s a two- or three-month average of your blood sugar.
Glucose Fasting Blood Sugar Test:
• Glucose fasting blood sugar test It measures fasting blood sugar.
For 8 hours before the test, you can only consume water.
• Glucose tolerance test (OGTT).
This test analyses your blood glucose levels two hours before and after a sugary meal.
Diabetes Type 2 Therapy Changes in lifestyle and medicine are used to manage type 2 diabetes.
Modify your way of You may be able to control your blood sugar levels only with food and activity.
• Weight loss! Losing weight helps:
Obesity loss of at least 7% appears optimal.

A 180-pound person may lower their blood sugar by 13 pounds.
Eating healthful foods and controlling portion sizes are intelligent ways to lose weight.
• Eating well Diabetes type 2 has no diet:
Learn about carbohydrates and create a food plan with a licenced nutritionist.
- Reduce calorie intake
A diet rich in vegetables and fruits and low in processed carbohydrates will help you lose weight.
• Exercise:
Get 30-60 minutes of exercise daily. Take a stroll, ride a bike or swim.
Combine it with yoga or weightlifting for further strength.
You may need a snack before an exercise if you are on a blood sugar-lowering prescription.
• Keep an eye on your sugar:
When to check your blood sugar, especially if you are on insulin, ask your doctor.
You may require medicine if lifestyle modifications do not work.
• Metformin (Fortamet, Glucophage, Glumetza, Riomet).
This is frequently the first drug prescribed for T2D.
In addition to lowering glucose production, it improves insulin response.
• Sulfonylureas:
This class of medicines increases insulin production.
For example, Amaryl contains glimepiride (DiaBeta, Micronase).
• Meglitinides:
They operate quicker than sulfonylureas at increasing insulin production.
Natiglinide (Starlix) with repaglinide (Prandini).
• Thiazolidinediones. They increase insulin sensitivity, like metformin.
Pioglitazone (Actos):
Pioglitazone (Actos) or rosiglitazone (Avandia).
It’s a good idea to see your doctor before starting any new medication.
DPP-4 inhibitors can cause joint pain and pancreatic inflammation.
GLP-1 agonists These needle-based treatments inhibit digestion and reduce blood sugar.
• SGLT2 inhibitors:
These aid in glucosuria removal by the kidney.
Your doctor could prescribe Invokana, dapagliflozin, or empagliflozin (Jardiance).
Heart failure hospitalisation and mortality have been reduced with empagliflozin.
• Insulin:
Overnight insulin detemir (Levemir) or glargine injections (Lantus).
A healthier lifestyle and taking your medication as advised may not help.
That doesn’t make you a bad guy!
Due to the nature of Diabetes, many patients require many medications.
Combination Treatment:
Combination treatment uses multiple medications to control your type 2 diabetes.
With your doctor, determine the optimum combination for you.
You usually retain metformin and add something else.
Depending on your scenario, it may vary.
Blood Sugar Rises:
Several drugs reduce blood sugar spikes (hyperglycemia) after meals.
Others work better in preventing blood sugar dips (hypoglycaemia).
Some may assist with Diabetes, weight reduction, cholesterol, and Diabetes.
Discuss any adverse effects with your doctor.
Cost may also be a factor:
This will need to be factored in if you take any other prescription medicine.
With a new medicine combination, you’ll require more frequent visits.
Drugs/Medication:
Not everyone needs two drugs to regulate their blood sugar.
Or the two-drug combo may only work temporarily.
A third non-insulin medication or insulin treatment may be considered if this occurs.
Diabetic Prevention A healthy lifestyle can help reduce diabetes risk.
• Slim down:
Reduce your risk of type 2 diabetes by 7-10% by losing weight.
• Get going:
Walking for 30 minutes a day reduces risk by roughly a third.
• Eat well:
Avoid refined carbohydrates, fizzy drinks, trans and saturated fats.
Limit red and processed meat.
Quit smoking:
• Quit smoking and talk to your doctor about losing weight.
Diabetic Complications In the long run, elevated blood sugar can harm and harm your:
• Cardiovascular system heart disease and stroke risk increases up to five-fold.
Blood artery blockage (atherosclerosis) and chest discomfort are significant risks (angina).
• Kidneys:
Dialysis or a kidney transplant may be required if your kidneys are damaged or fail.
• Eyes:
Your eyes’ tiny blood vessels might be damaged by high blood sugar (retinopathy).
Non-treatment can lead to blindness.
• Nerves:
This can cause digestive, foot, and sexual issues.
• Skin:
Wounds heal slowly and might become infected due to decreased blood circulation.
• Pregnancy:
Miscarriage, stillbirth, and birth defects are more common in diabetic women.
-
Sleep:
You may develop sleep apnea, a disorder in which you stop breathing while sleeping.
• Hearing:
People with hearing issues are more likely to get them, but why?
• Brain:
High blood sugar damages the brain and increases the risk of Alzheimer’s.
• Depression:
The condition doubles the risk of depression.
- Managing your type 2 diabetes:
Managing your type 2 diabetes will help you prevent these consequences. ·
Take your diabetic meds or insulin as prescribed.
• Check your sugar.
• Eat well and don’t miss meals.
• Visit your doctor periodically to monitor early warning symptoms.
Create a Healthcare Team Physicians that specialise in diabetes management include:
Questions To Ask?
Diabetes educators and managers include podiatrists, ophthalmologists, and dentists.
Diabetic Questions to Ask Your Doctor When just diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, ask your doctor these questions.
1. Does Diabetes increase my chance of other health issues?
2. Should I regularly see other doctors, such as an eye doctor?
3. How often should I check my blood sugar, and what should I do if it’s too high or low?
4. Are there any new diabetic meds I can try?
5. Does having Diabetes mean I can’t eat my favourite foods?
6. How can exercise help with Diabetes?
What weight loss is required to improve my health if I’m overweight?
7. Do my kids have a higher chance of contracting it?
8. What role does nutrition play in Diabetes?
Does it matter if I feel okay on my medication days?
I hope you enjoyed the Symptoms and Complications Of Type 2 Diabetic.
Please leave your questions and comments below and I will gladly respond.



There are a few people in this Earth that have diabetes, my mom included but I do not think that it is type two. I will still be sure to share this article with her. Maybe it will help her out so thank you for this. I truly appreciate this message.
Thank You for your comment Aubin
Yes, there are lots of people with diabetes. In my family, my cousin has diabetes type 1 my mother had diabetes type 2 and I also have diabetes type 2.
It usually runs in the family or it comes later in life that you get diabetes.
Thanks again for your comment
Elke
There seems to be a growing pandemic of Type 2 diabetes around the world and I can understand why. We seem to have developed a very sedentary lifestyle and lots of high-carb and sugar foods to eat daily. We also view this as our reward for working hard, or if we celebrate an event such as a birthday or Christmas.
How vigorous does the exercise need to be daily to fend off diabetes?
Thank You for Yours Comment Lily,
I am a diabetic and found it very hard over the Christmas Period to keep my sugar down. Now being in 2022 I will have to get back to my routine of avoiding sugar.
Regarding the exercise I would start with a 20 minute walk and then increase to 30 – 40 minutes. It does not have to be strenuous exercise.
It also good to ride a bike or exercise bike if you have difficulty walking.
My diabetic educated tells me everything in moderation that includes exercise as well.
Hope this helps
Elke